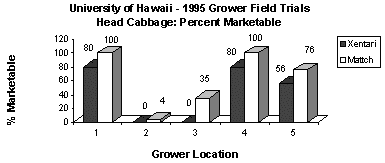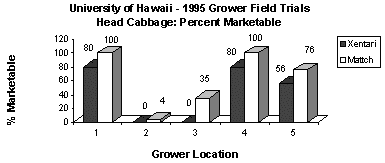(HAWAII) VEGETABLES
Recommendations for Use
For Control of Caterpillar Pests in Vegetables
Including Diamondback Moths, Loopers, Armyworms,
Imported Cabbageworms and Heliothis/Helicoverpa Species
(For Use or Distribution in the State of Hawaii)
Mattch Bioinsecticide belongs to a new class of increased
residual, high potency, biological insecticides utilizing Mycogen's
CellCap® Encapsulation System. The biotoxins in Mattch are
effective against a broad range of major caterpillar pests, but
are low in toxicity to beneficial insects and mammals.
- Mode of Action: Mattch contains two delta endotoxins
which are potent insect stomach poisons and must be eaten by the
target insect to be effective. Once eaten the biotoxins disrupt
the larva's digestive system, resulting in starvation and death
one to five days later. Mattch is most effective against 1st and
2nd instar caterpillar larvae.
- CellCap Encapsulation System: Mattch utilizes the CellCap
Encapsulation System, a patented process which allows for an easy
handling formulation and improves field performance and shelf
life. Conventional Bt's degrade rapidly on the leaf surface due
to adverse effects of heat, sunlight and other environmental factors.
This degradation renders the biotoxin ineffective against feeding
larvae. Mattch uses biological microcapsules to protect the biotoxins
from environmental degradation. As a result Mattch provides greater
foliar persistence than traditional Bt products. Mattch delivers
more consistent, longer lasting control of caterpillar pests.
- Toxins: Mattch contains two delta endotoxins of Bacillus
thuringiensis. Cry1A(c) of B. thuringiensis variety
kurstaki was selected based on its superior activity on
diamondback moth, cabbage looper, tobacco budworm and tomato fruitworm.
Cry1C of B. thuringiensis variety aizawai was selected
based on its superior activity on armyworms, cabbage looper and
diamondback moth larvae which in some areas are resistant to B.
thuringiensis variety kurstaki.
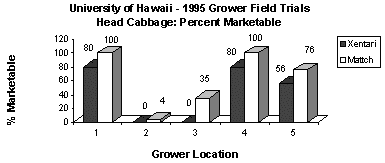

USE GUIDELINES
- Stand alone: Use Mattch at 2.0 quarts per acre for
most stand alone applications. When diamondback moth is the primary
pest, a lower rate of 1.5 quarts per acre normally provides excellent
control.
- Tank mix: In most situations, Mattch should be applied
at 1.0 quart per acre when tank mixed with other pesticides which
are also directed at the same lepidopteran pest(s).
- Uniform and complete coverage of the foliage where larvae
are feeding is essential to good control. Application water volume
should be sufficient to ensure good coverage, a minimum of 20
GPA is recommended. For aerial application, use a minimum of 5
gallons of total spray volume per acre.
- The addition of an appropriately labeled spreader-sticker
is recommended to improve coverage and deposition on crop foliage.
- When tank mixing Mattch with other insecticides, comply with
all label instructions of all products which are included.
STEPS FOR SUCCESSFUL RESULTS
- Scout for eggs and apply Mattch when newly hatched larvae
are present. Mattch is most effective when applications are targeted
at newly hatched, 1st and 2nd instar larvae and before the insect
can penetrate inside the plant's protective foliage, stems, or
fruit.
- Scout fields 3 to 5 days after application to determine the
effectiveness of the application, and to assess the need for subsequent
applications.
- Retreat as needed to control reinfesting or increasing pest
populations. More than one application per week may be necessary
when larval populations are high.
- Reapply Mattch if rain occurs within six hours after treatment.
Always read and carefully follow all product labels.
Mattch is a trademark and CellCap is a registered trademark of
Mycogen Corporation.
DiPel and Xentari are trademarks of Abbott Laboratories.
Mattch EPA #53219-10 MYC. JJ#2199HI 10/95